At the crossroad of East and West, Turkey’s history is as diverse as the country itself. It’s a story of ancient Anatolia, Byzantine glory, Ottoman imperialism, and modern republicism.
This is an in-depth look at the way this country has always played host to numerous civilizations, empires, and cultural waves.
By looking at its archaeological sites, love travel more buildings, cultural achievements, and social transformations, we can identify the patterns that made this country into what it is today!

Turkey History Timeline
7500 BCE: Ancient civilizations, including the Hittites, settle in Anatolia.
Rise of Kingdoms: Lydia and Phrygia gain prominence.
547 BCE: Persian Empire gains control over the region.
334 BCE: Conquest by Alexander the Great.
133 BCE: Roman Empire takes control.
330 CE: Constantinople becomes the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire).
11th Century: Seljuk Turks arrive and bring Islamic influence.
1453: Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire under Sultan Mehmed II.
16th Century: Ottoman Empire reaches its peak under Suleiman the Magnificent.
18th-19th Centuries: Decline of the Ottoman Empire.
1919-1923: Turkish War of Independence led by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk.
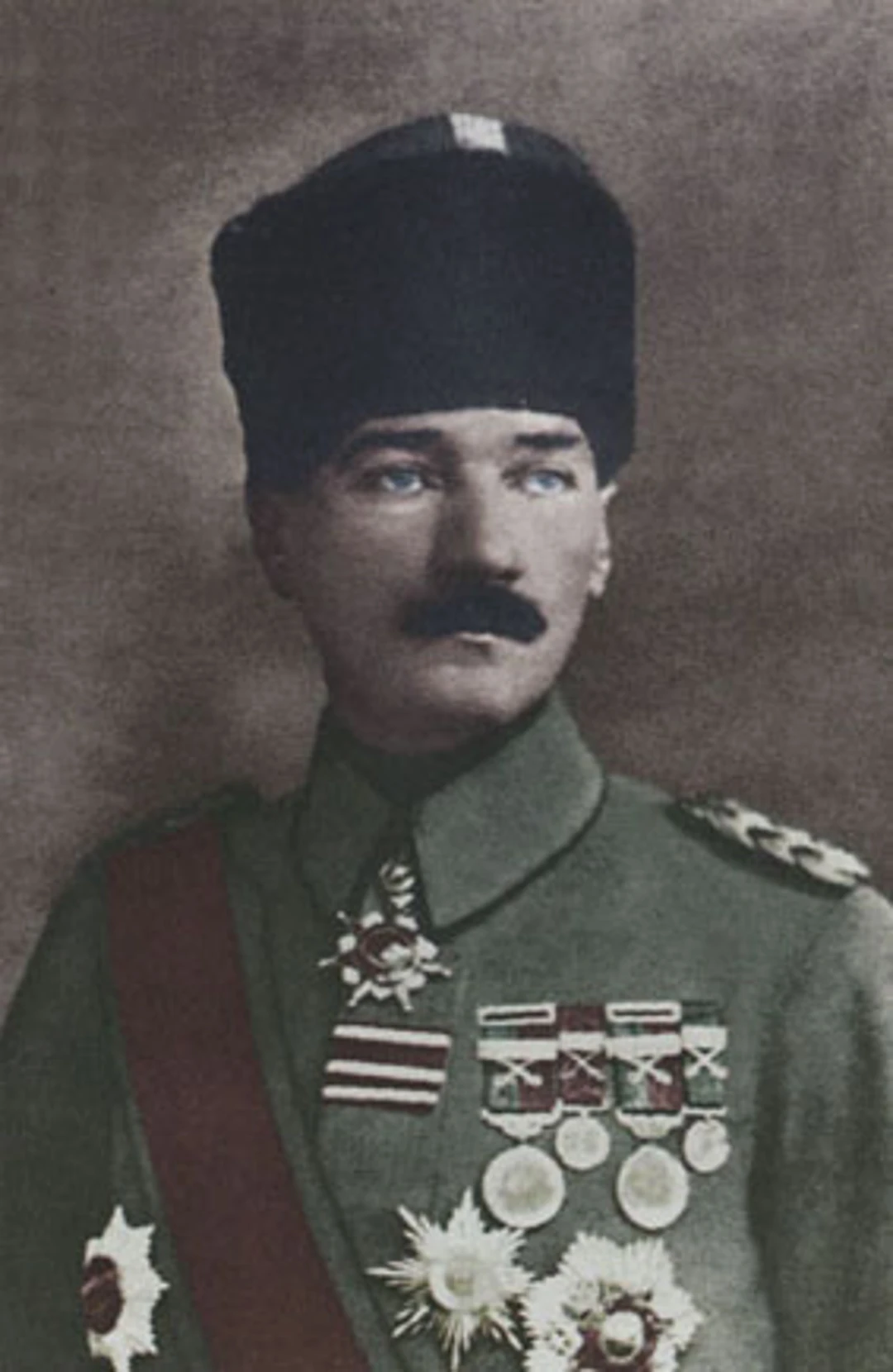

October 29, 1923: Establishment of the Republic of Turkey.
1923-1938: Atatürk’s modernization reforms.
1952: Turkey joins NATO.
1999: Turkey becomes a candidate for European Union membership.
2024: Turkey remains a vital geopolitical bridge between East and West.
Ancient Anatolian Civilizations (Pre-Islamic Period)
Anatolia — modern-day Turkey — is one of the oldest and most interesting places in the world. Its inhabitants took big steps really early, like the structures at Göbekli Tepe (the world’s oldest known temple, built around 7500 BCE). The Hittites were one of the earliest to form a major state, doing so around 1750 BCE. They were quite sophisticated, too — they signed one of the oldest peace treaties we have with the Egyptians!
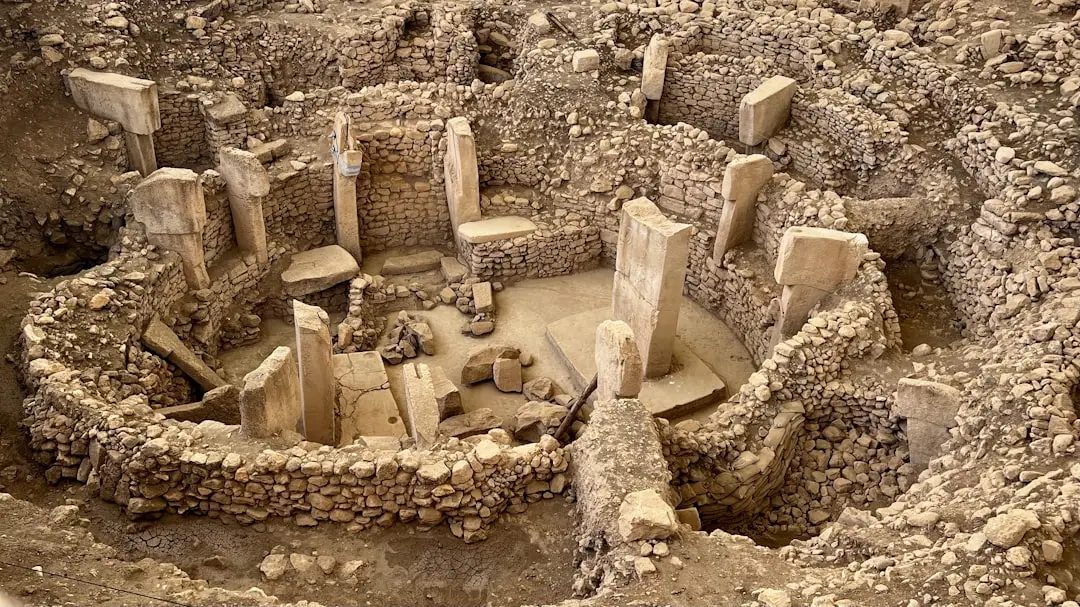

The Assyrians and Urartians enter the stage in eastern Anatolia, erecting amazing fortresses that are still standing today. Croesus and his rich Lydian kingdom introduce the world’s first coins in western Anatolia, permanently altering how people engage in trade. The Phrygians, who used rock to carve out many monuments and the king Midas legend, and the Greeks, who settled the coast and create amazing cities like Ephesus and Miletus.
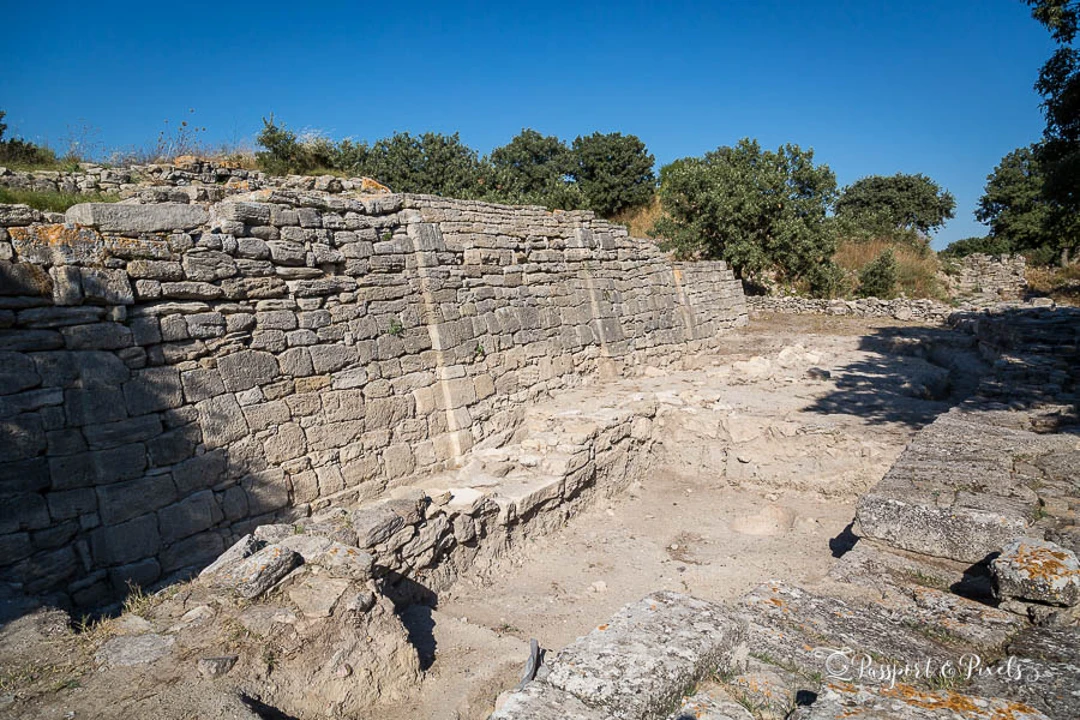
And these ancient cities were much more than simple living spaces; they were hubs of art, education, and development. Ephesus grew to be one of the largest cities in the ancient world, with an enormous library, and a temple that was so grand that it was listed as one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The archaeological sites we can explore today, such as the walls of Troy or the first city roads of Çatalhöyük, provide insights into what life was like for these impressive civilizations.

And each one of those cultures left impressive works of art and infrastructure for us to ponder. Beautiful Hittite sculptures. IntricateUrartian metalwork. Stunning Greek temples. All of these can still begazed upon in present-day Turkey, providing us with a glimpse into how people used to live, work, and worship thousands of years ago — only the entire country is an open-air museum! And best of all, archaeologists are still uncovering new ruins and sites each year. It’s simply amazing.
Because Anatolia lay between Europe and Asia, the region acted as a crossroads for a wide variety of cultures and ideas. The Persians arrived next, while in 334 BCE it was conquered by Alexander the Great, blending Eastern and Western culturesin an unusual way. This eclectic mix of civilizations would remain a hallmark of Turkiye in the centuries and millennia to come, down to the present.

The Byzantine and Roman Influence
Rome’s influence would stretch into Turkey beginning in 133 BC, with incredible results. When in 330 AD Emperor Constantine moved the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire from Rome to Byzantium (and renamed it Constantinople), he built one of the most interesting cities in world history. It rapidly turned into a stunningly rich, powerful, and cultured city that would thrive for over a thousand years as the center of the Byzantine Empire.
The Hagia Sophia is the most breathtaking example of Byzantine architecture. It continues to awe visitors. Constructed in the 6th century under Emperor Justinian, the church was the world’s largest for almost a thousand years. With its huge dome appearing to float, the building has been a church and a mosque during its rich and storied history.
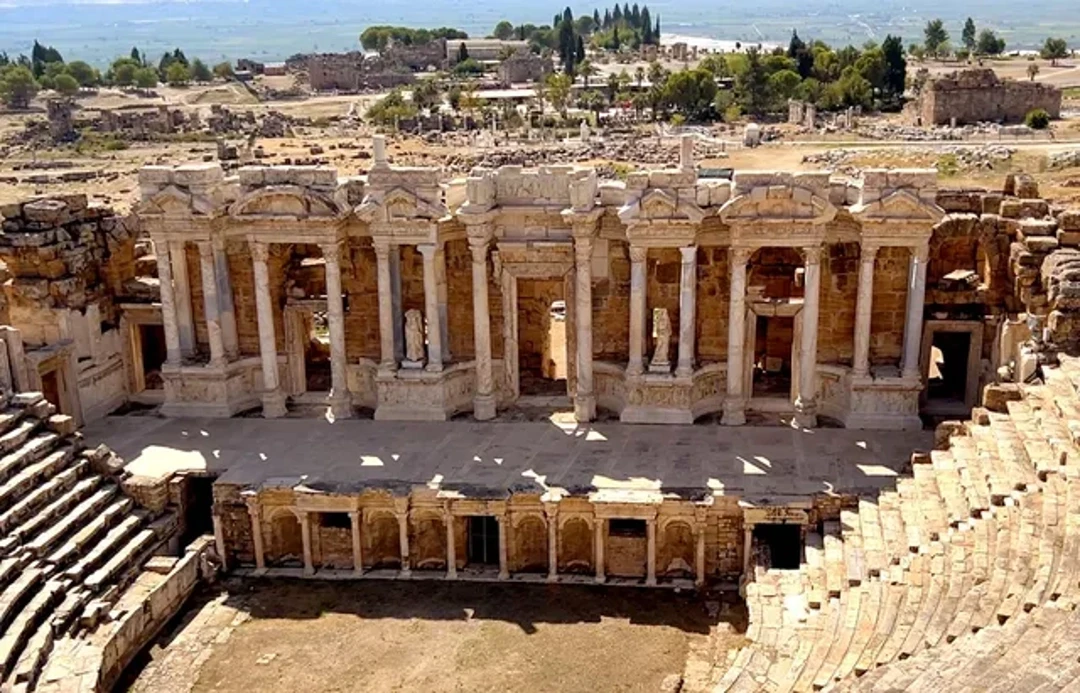

This country was covered in Roman and Byzantine ruins — and ruins of Roman and Byzantine cities. You can wander the old streets of Ephesus (home to one of the best-preserved Roman theaters on Earth); at Hierapolis, you can soak in the same Roman baths that people used thousands of years ago, with naturally heated mineral water.
Byzantine art combined the grand styles of Rome with Christianity, which, as you can imagine, made for some beautiful art. Just look at the mosaics in the Church of Chora in Istanbul to see how talented Byzantine artists were. These vivid scenes depict biblical stories as well as daily life in Byzantium.
The Byzantine Empire was not all nice buildings and artwork. It was a translator and a conduit that helped ideas and knowledge translate back and forth from East to West. Greek was predominantly spoken but Latin and Armenian were common as well. The city’s legacy endures in the country’s food and architecture and culture. It’s incredible how wide and deep those roots ran.
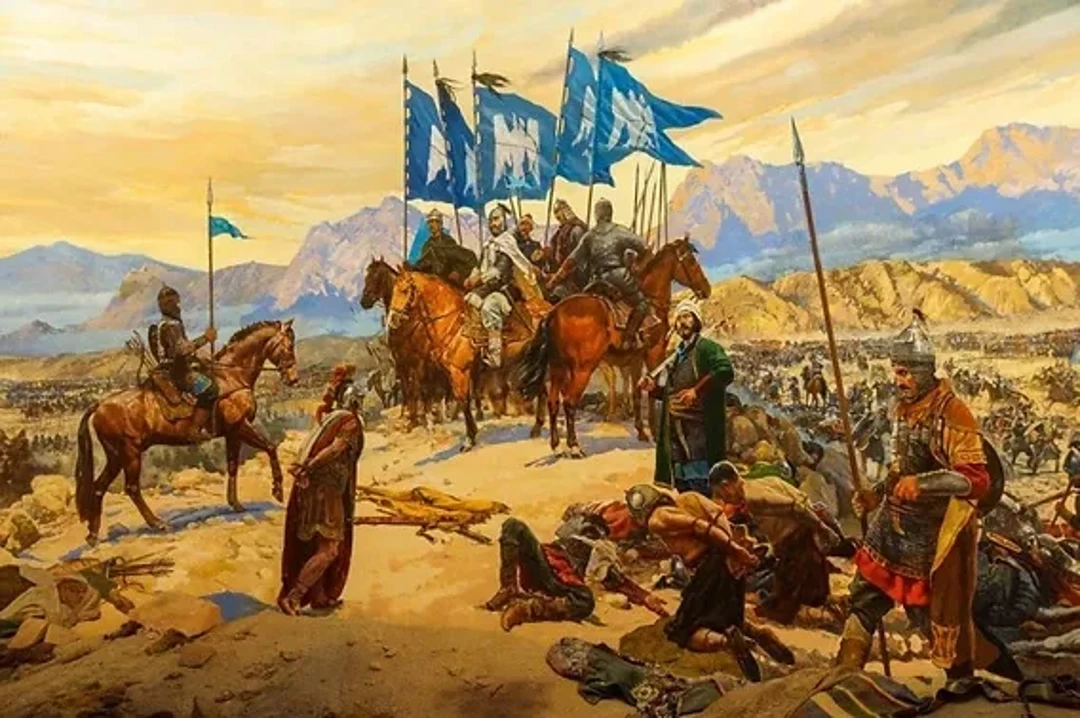
Major Events of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire was founded by Osman I, a tribal leader who began conquering territory in the region and was eventually able to establish a state that grew into one of the world’s most powerful empires. The empire’s climax was in 1453 when Sultan Mehmed II conquered the city, renamed it Istanbul, and made it his new capital. This transformed the Ottomans from a regional power into an imperial power that would influence the world for centuries.
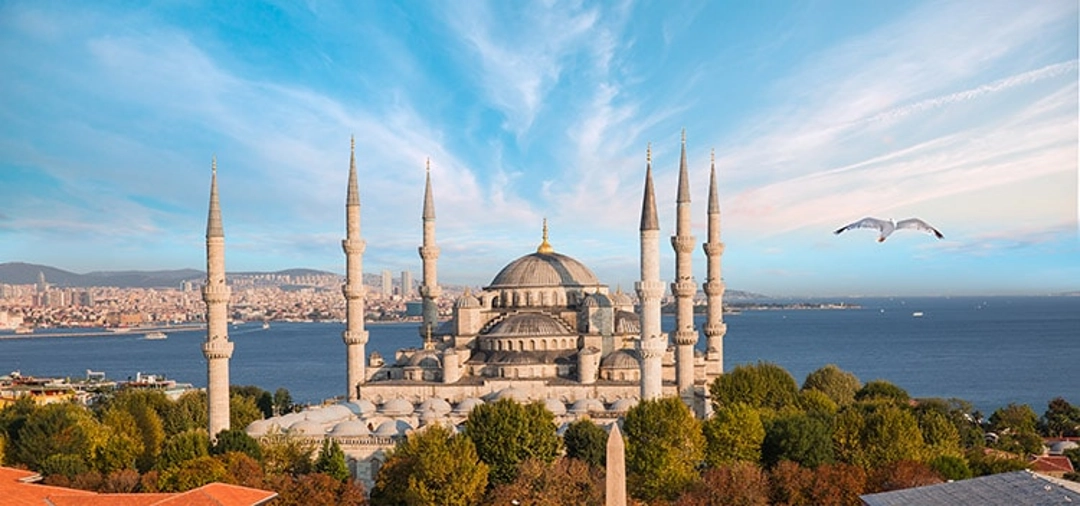
The empire’s golden age came under Suleiman the Magnificent in the 16th century. His armies made it up to the gates of Vienna in Europe, and its navy ruled the Mediterranean Sea. The empire wasn’t only a military power, though. It produced some incredible art, science, and architecture, including the Blue Mosque, and made discoveries in fields like math and medicine.
Life was pretty unique in the Ottoman Empire compared to life in other parts of 16th-century Europe. It was a very diverse place — people of all religions and ethnicities lived there relatively harmoniously. Within a single city, like Istanbul, you could find neighborhoods where Christians, Jews, and Muslims lived side by side. The Ottomans knew what they were doing when it came to running an empire, and they established systems for educating their people, conducting trade, and governing that were far more advanced than those of neighboring nations.

However, as happens with all empires over time, the Ottomans eventually started to fall behind. By the 1700s and 1800s, European states were growing in power and exhibiting more technological and intellectual sophistication, whereas the Ottoman Empire was failing to keep pace. The empire attempted to modernize by implementing a series of reforms known as the Tanzimat, but these efforts could not prevent the gradual disintegration of the empire.
World War I was the death knell for the Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans were allied with Germany and this alliance ended up being on the losing side of the war. The empire, which had ruled for over 600 years, was no more in 1922, and things were then reorganized into the Republic of Turkey.

The Birth of Modern Turkey and Key Highlights of Atatürk’s Reforms
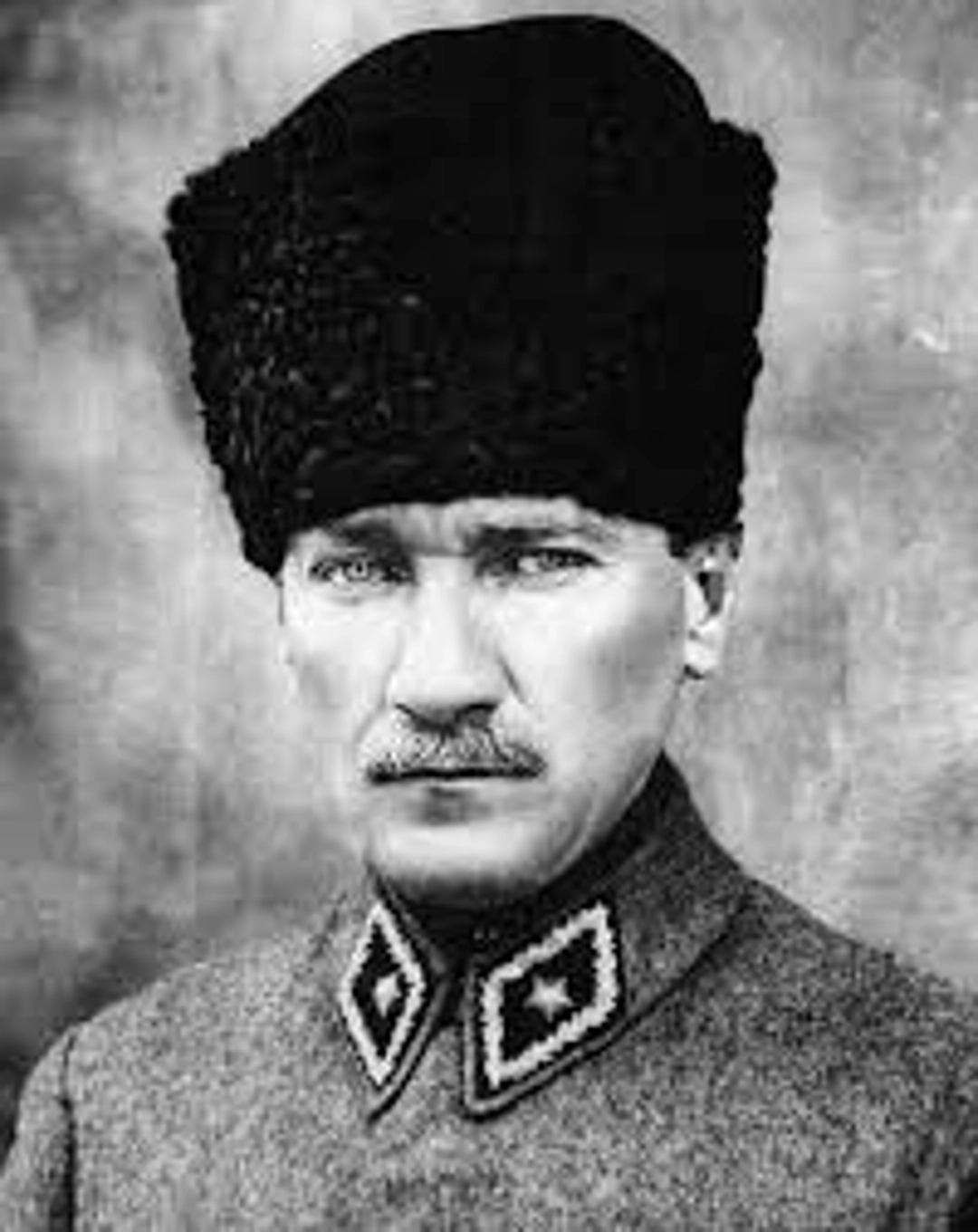
Turkey became a nation in the early 20th century thanks to an extraordinary war of independence. In the wake of World War I, the Ottoman Empire was being taken apart by foreign powers. But a courageous army officer named Mustafa Kemal (who would later become known as Atatürk) rose up as a leader and rallied the Turkish people to fight against foreign rule. This war, which lasted from 1919 to 1923, ended with a truly remarkable Turkish victory and the establishment of the Republic of Turkey on October 29, 1923.
When Atatürk became the first president of Turkey, he realized that the country had to change a lot to modernize. One of his most radical ideas was to turn Turkey into a secular country by distinguishing and separating religion from government – a major shift from the days of the Ottoman Empire! He also gave women the same rights as men, including the right to vote and the freedom to run for office. Turkey was one of the first countries in the world to do this.

Education was another. He revolutionized the educational system by replacing the Arabic script with the new alphabet of Latin characters. Nowadays, Turks no longer study the difficult Arabic script in school and can read and write in their language in a matter of days. What do you think Is every citizen in the country having to learn a new alphabet? Yes, that’s correct, and as you can guess, literacy rates skyrocketed from this bold move!
But Atatürk’s reforms went further. Adatürk replaced the old Islamic legal system with an entirely new European-based legal system. He urged everyone to dress in the Western style and also implemented a Western calendar and clock. Turkey now resembled the world more closely.
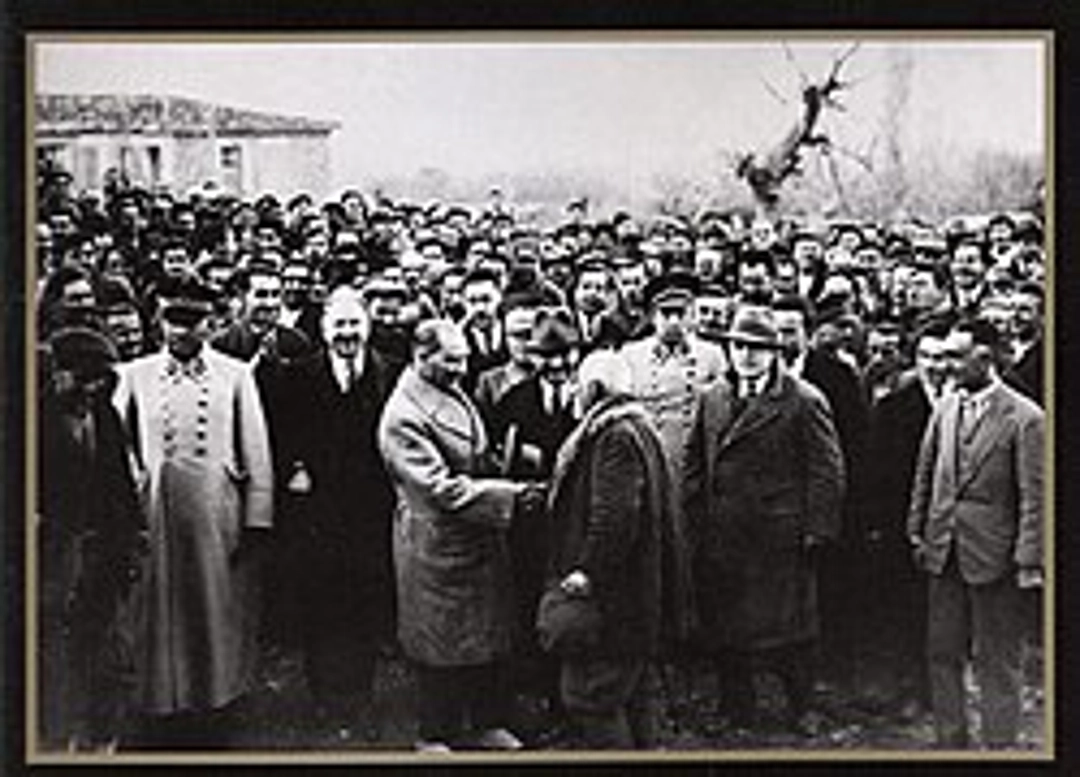

The effects of his reforms were massive, and they continue to impact Turkey today. I mean, in just a few years, the nation went from being a territory in a crumbling empire to a modern republic where women had the right to vote, everyone spoke the same language, and people were suddenly granted freedoms they never had! It’s one of the most amazing transitions ever!
Cultural Developments Over Time
Turkey as a culture is a wonderful mosaic that has developed over millennia! The art, music, cuisine, and traditions we can experience in modern-day Turkey is the result of all the different ethnic groups that have lived in this land for the last several thousand years. Everyone from the Hittites to the Ottomans to the modern Republic has had their own unique input added to this cultural quilt.
When the Seljuk Turks came here in the 11th century they introduced some amazing and new architectural styles. Do you know those beautiful buildings they built with all of those geometric designs and calligraphy? They also brought new forms of poetry and literature that would affect Turkish culture for centuries. The way they decorate buildings with tiles of various shades of blue is also something that is still prominent in historic buildings around here.

During the Ottoman era, Turkish art and architecture reached new levels of sophistication. Beautiful art and architecture developed, with elaborate and detailed decorations adorning most objects in this society. Its miniature paintings are well known for depicting scenes from the royal court, and their calligraphy was so stunning it turned calligraphy into an art form. Turkish rugs grew in popularity and music was highly valued, with an orchestra and musicians on retainer by the sultan.
Food is another fabulous aspect of Turkish culture. It’s something that has been refined and perfected for centuries. Every region has its specialties, but things like kebabs, pide (think “Turkish pizza”), and baklava are nationwide staples. The Ottomans used to have and hundreds of chefs in the palace, who would specialize in certain culinary types.

Modern Turkey, on the other hand, has excelled at incorporating traditional disciplines into modern formats. This can be seen in fashion, in music (where traditional Turkish instruments might be used in a pop song), or even in art (where centuries-old carpet designs might be the inspiration for a modern piece). Turkish coffee culture has taken on a modern twist too, with the traditional coffee houses coexisting with modern cafes.
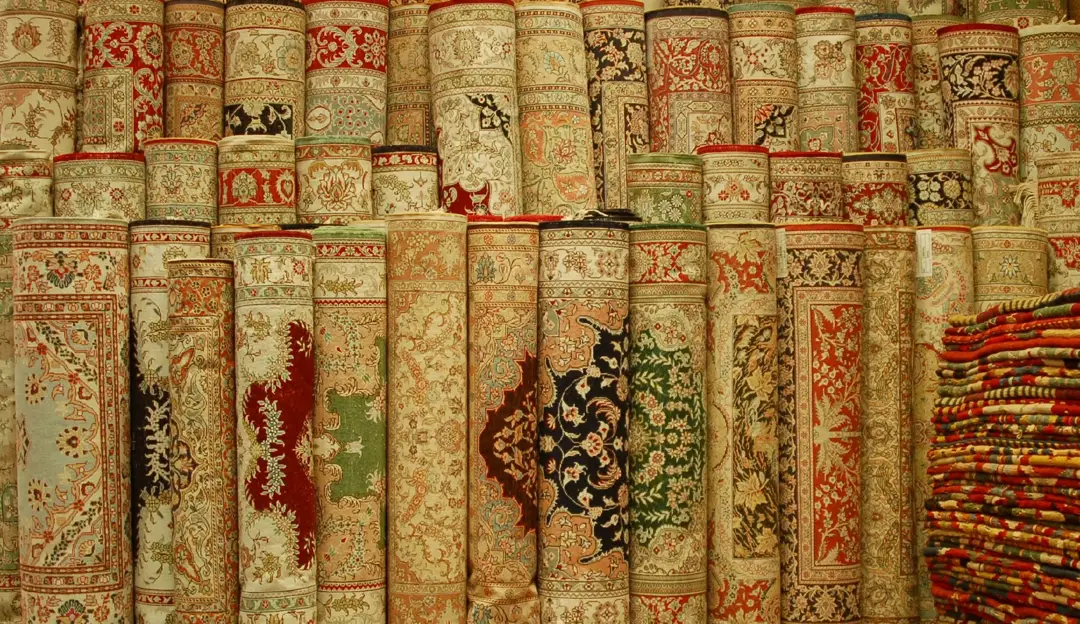

While new art forms are also flourishing in modern Turkey, traditional crafts have by no means been replaced. Carpets are still woven using centuries-old methods, ceramics are still carefully painted, and paper is still marbled (in a technique known as ebru). And the best part? These traditional crafts are still being practiced to this day, not just by artists and inside museum walls, but by ordinary people learning from their parents or grandparents.
Today’s Turkish culture is a living testament to this balance, as it blends the incumbent traditions and influences of the past with the hip and happening trends of the present. For example, you may spot a person strolling through an ancient bazaar buying spices in modern-day attire or maybe even experience the music of Turkey being played on what appears to be a Western instrument. It is truly a country of old and new and all its has to offer.
Role of Ethnic Minorities and Women in Turkish History
Throughout its history, Turkey has hosted various ethnic populations that have brought their own stories to the cultural table. The Armenians for example, were skilled artisans, and wielded substantial influence in trade and architecture during the Ottoman years. Greek communities graced seaside towns for millennia, adding to the culture and trading and maritime knowledge. The Kurds have continued to keep their customs and culture alive, contributing heavily to Turkey’s mosaic, particularly in the east.
But it wasn’t always easy. During the late Ottoman Empire and early republic, many of the ethnic populations shifted in Turkey, as some groups struggled during this period and ended up emigrating from the country to other destinations. However, you can still notice distinct ethnic foods, music, and architecture in Turkey from a variety of groups.
The role of women in Turkish history is actually quite interesting. There are some really fascinating stories. For example, one of the most powerful women in Ottoman history, Hürrem Sultan (also known as Roxelana), was a slave who married Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent. She was able to influence political decisions and commissioned many public buildings that still stand. In fact, women in the Ottoman palace had a lot of power. They would even advise the sultans and ran a number of charitable foundations.
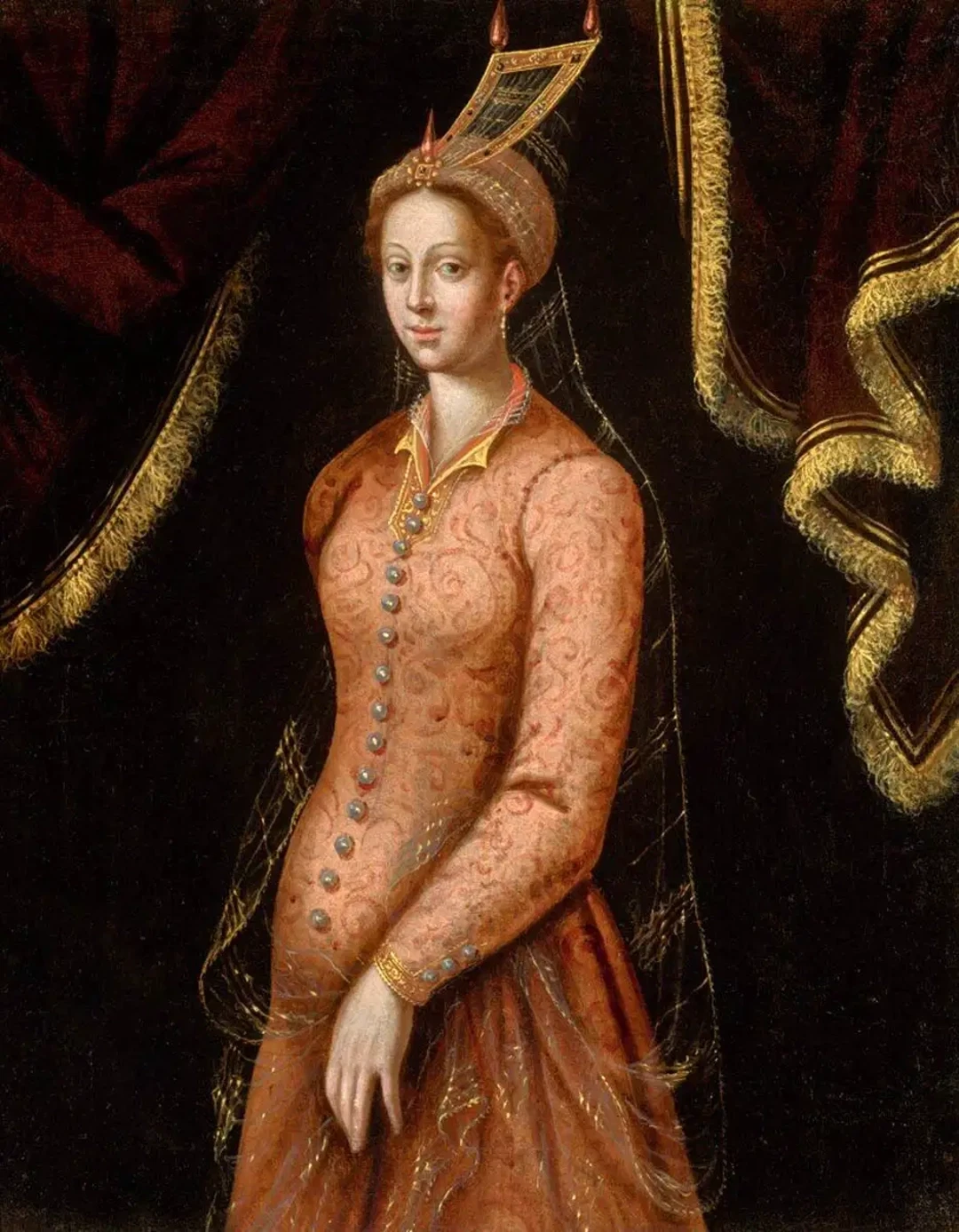

The real breakthrough for women’s rights occurred after the country was established as a Republic. In 1934, Atatürk granted women the right to vote, which was several years before much of Europe did the same! This allowed women to vote, receive an education, choose a career, and run for office. In fact, Sabiha Gökçen was the world’s first female combat pilot and Halide Edip Adıvar was a renowned writer and political activist.
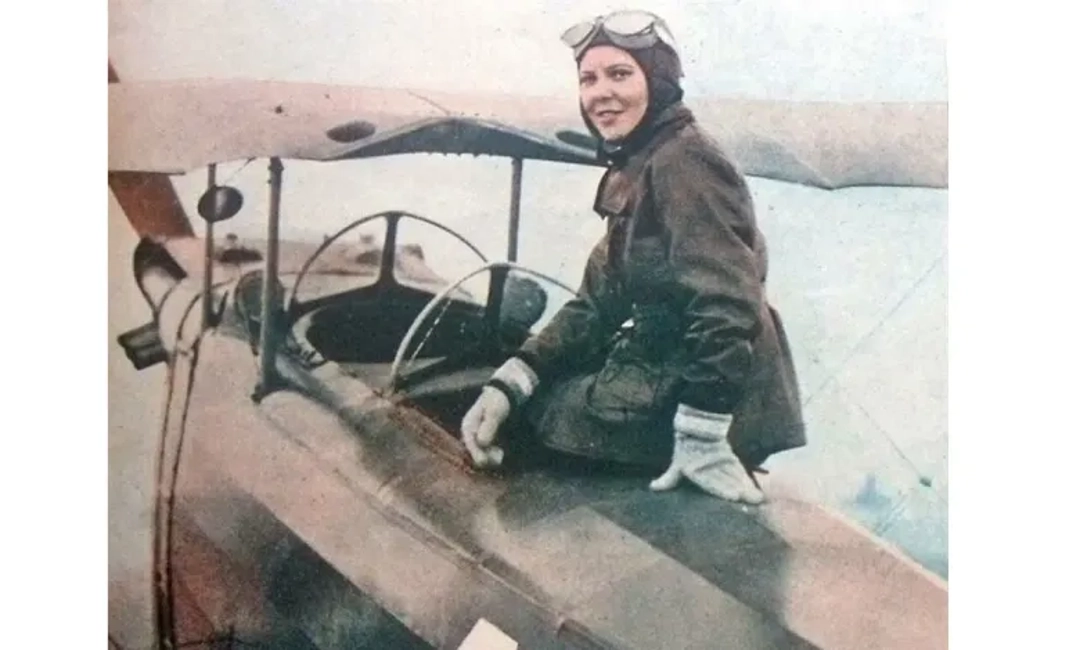

Modern Turkey, however, is a much different place for women. Nowadays, women in Turkey are presidents of corporations, professors at universities, and judges and politicians. However, the country has a ways to go. Like many places, gender equality is stronger in the cities than in rural area.
The story of minorities and women in Turkey is still being written. New laws and shifting attitudes are making it better for all. Many of today’s youth embrace their dual identity and seek to maintain their traditional ways while being a part of Turkey today.
Geopolitical Role and Relationships
Turkey’s location is incredibly strategic for global politics – it serves essentially as a bridge between Europe and Asia! As a result, it has been quite influential in much of the world’s history. Its membership in NATO since 1952 has helped solidify its role as an ally to many Western countries, especially theUnited States and its allies during the Cold War and today.

Turkey’s journey with the European Union has been complicated. While the country has been applying to join the EU since 1987, and was made an official candidate in 1999, the experience has had its share of twists and turns. Though the Turkish still aspire to becoming part of the EU, there’s still a ways to go before that could become a reality.
Neighborhood relationships have been a bit of a rollercoaster. In a few places relations are tinged with security and trade, Turkey cooperates with most of its near neighbors. For instance, Turkey and Greece don’t get along on everything, yet they also have a lot of areas where they do cooperate.
Turkey also helps keep the region secure. But if it helps, just imagine Turkey as a giant stability anchor in a very unstable area! The country takes on a lot of big tasks in the region, such as handling refugees and going on peacekeeping missions.

Again, Turkey’s geographic location makes it very central when it comes to energy politics. Many oil and gas pipelines pass through the country, turning it into a bit of an energy superhighway between the middleeast and Europe. This, in turn, has allowed Turkey to foster stronger ties with countries that either produce or consume energy.
Over the last several years, Turkey has tried to flex its muscles more on the world stage. You see it from their increasing involvement in international bodies to their attempts to mediate in the problems of their region. They have also started reaching out to countries in Africa and Asia, signaling they want to have a positive relationship with everyone, not just their traditional allies.
Recommended Sights, Books, and Movies About Turkish History
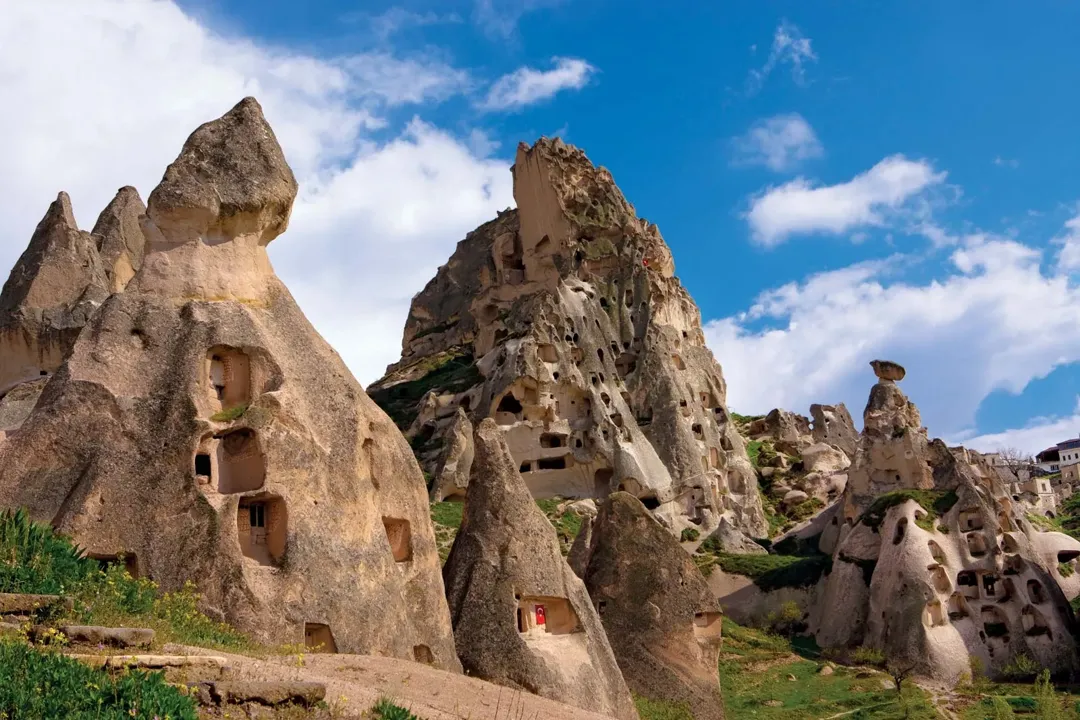
The historical attractions in Turkey are out of this world!The best historical placesin Turkey are actually like wandering through a giant history book.Take Istanbul, for example – simply walk through Hagia Sophia and Topkapi Palace! Meanwhile, the ruins of Ephesus house an enormous theater and gorgeous Library of Celsus, and Cappadocia’s fairy chimneys and underground cities are the dazzling remnants of early Christians.

If you’re a history buff looking to read more, I recommend “Lords of the Horizons” by Jason Goodwin. It’s a really good story about the Ottoman Empire that’s very approachable. “Turkey: A Short History” by Norman Stoneis a good short history book, and “Crescent and Star” by Stephen Kinzeropt is an excellent book about modern Turkey.
Turkish historical films are excellent. “Conquest 1453” is about the fall of Constantinople, “The Last Emperor” is based on the fall of the Ottoman Empire, and “Once Upon a Time in Anatolia” can give you a sense of what life is like in the country and even touches on a little history too.
Make sure you visit the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations in Ankara — it’s a time warp that will transport you back to this country’s distant past! The archaeological site of Göbekli Tepe is just mind-blowing — it’s the oldest temple complex ever found in the world! And if you’re into Ottoman history, the palaces in Istanbul, especially Dolmabahce Palace will give you a look at how the sultans lived in the modern era during their final era.
For a comprehensive perspective on Turkey’s cultural history, head to Istanbul’s Turkish and Islamic Arts Museum. And remember: “The Turkish coffee trail” isn’t only about getting drunk–on the contrary, it’s a great introduction to Ottoman cultural history and Turkish hospitality!
Conclusion
Turkey’s story is so amazing – it really is like one big history book that keeps adding new pages! From the original temple builders at Göbekli Tepe to bustling, modern Turkey as it exists today, this place has seen its fair share of folks coming and going. Overall, how ancient societies, massive empires, and some very courageous reformers have influenced this engaging country.
Today, you can really see all this intertwined history playing out in Turkey in a unique way. It's the story of how different cultures can meet, mix, and create unique and beautiful things together.
As Turkey grows and evolves, one thing is certain: it will continue to be a place that inspires all kinds of travelers for decades to come.
